A basic framework for teaching critical thinking at school
by Terrell Heick
In What does critical thought mean?We have offered that “(c) RITITI thought is the suspension of judgment while identifying the underlying biases and hypotheses to draw precise conclusions”.
Of course, there are different definitions of critical thinking. The Philosophical Association American defines it As, “critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally, understand the logical link between ideas. This implies being active (rather than reactive) in your learning process, and it understands open -mindedness, curiosity and the ability to examine and assess ideas, arguments and points of view. »»
But understanding exactly what it is and means is different from the teaching of critical thinking-that is to say to constantly integrate it into your units, lessons and activities. Models and frames have always been useful to give meaning to the complex (or confusing– which is generally different from complex) Ideas. I also find them as a wonderful way to communicate any meaning creation.
In other words, models and executives can help to think and communicate concepts.
See also Examples of analogies for critical thinking
A framework incorporating critical thinking into your class
Obviously, the teaching of critical thinking in a class is different from “teaching it” outside one, just as it differs from active practice and the application of critical thinking skills in the “real world”. I have always taught students that critical thinking is something they do perfectly in their lives.
They analyze conspiracies and characters in films.
They create Make short videos.
They critical Relations and punishments and notes and video games.
They assess Their performance of favorite athletes and make judgments on music.
And so on. With this context away, take a look at the frame, okay?
Levels of integration of critical thinking
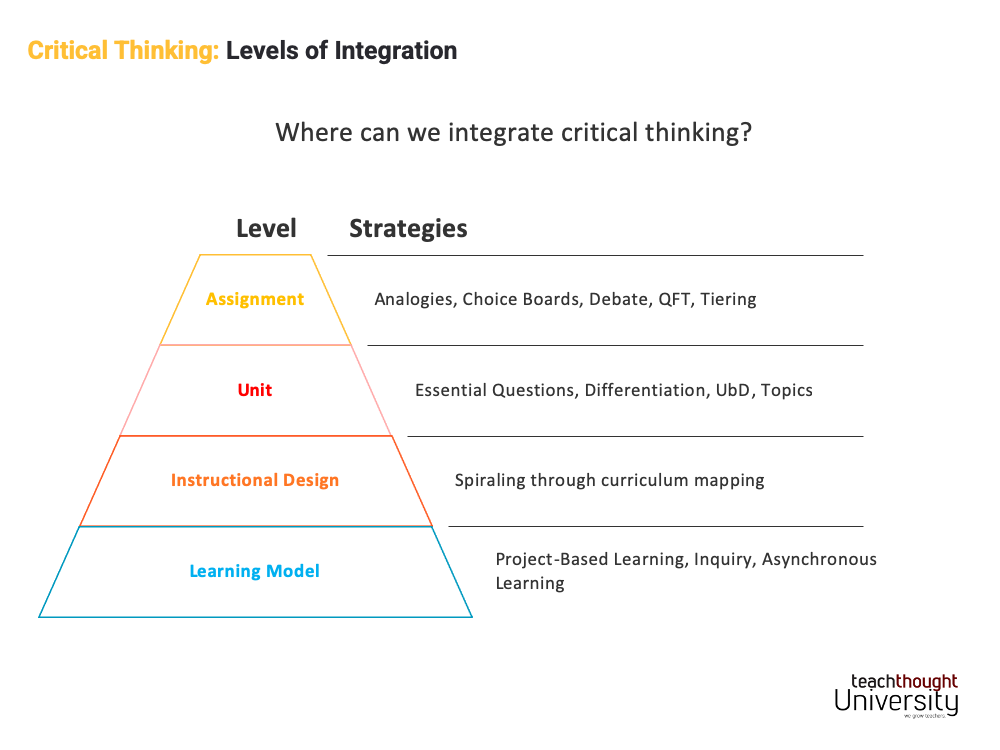
Preface: this message is necessarily incomplete. A complete guide for teaching critical thinking would be best done as a book or course rather as a blog article. The idea is to offer a way to think about teaching critical thinking.
Critical thinking can be made at …
In terms of mission Integration strategies
-Analogies (see also Analogies))
-Planches of choice
-Debate
-THE Question formulation technique
-Diation
Unit integration strategies
– Essential questions (see How to use essential questions))
-Differentiation (see also Ways to differentiate teaching))
-Conally by design (one of the elements of the UBD framework – back design, for example)
-Topics (that is, learning subjects that naturally encourage or even require critical thinking)
See also 6 Questions of critical thinking for any situation
Educational design level Integration strategies
-Spiration (in this case, in terms of program mapping)
In terms of learning model Integration strategies
– learning based on a project (see 25 questions to guide teaching with learning based on projects))
-PrenolSee 14 teaching strategies for learning based on surveys))
-Synchrone self -edited learning (see our Autonomous learning model))
(Tagstotranslate) Terry Heick



